Are you an expert on the history of East Germany?
Find out how much you know about life behind the Iron Curtain with our 20 question quiz.
Each question is multiple choice and is presented with a 60 second timer – so you’ll have to check your memory rather than dive into the books.
When you have answered each question you will also get a small description of the correct answer – so you might even learn something new along the way. Your final score will be presented at the end of the quiz, as well as the option to share your results via Facebook or Twitter to challenge your friends.
If you end up stumped, don’t worry, you can join one of our Republic of Fear tours and brush up for the next attempt…

#1. The flag of East Germany featured which two objects surrounded by a wreath of corn?
From 1949 until 1959, the East German flag was identical to the West German flag – the black-red-gold tricolour that had also been used during the Weimar Republic. However, ten years after the founding of the German Democractic Republic, the government amended this design by adding a hammer and compass inside a wrath of wheat – a symbol of the cooperation of the workers, farmers, and intelligensia.
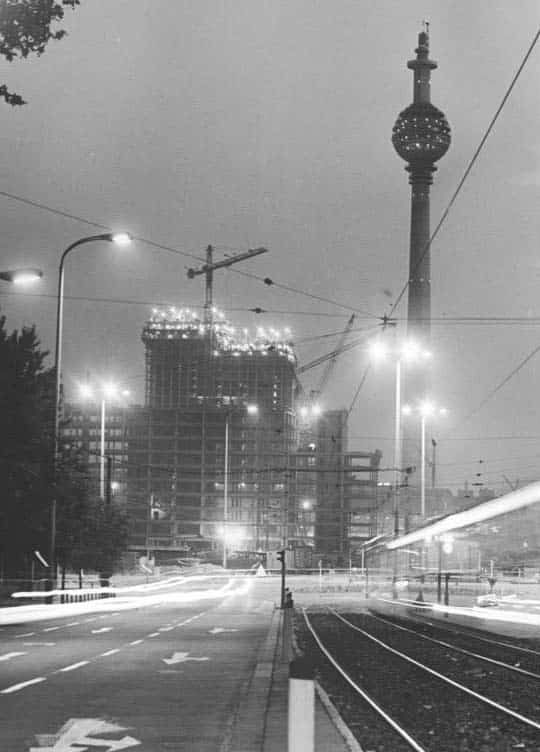

#2. Berlin’s iconic TV Tower was constructed with the help of engineers from which non-East Bloc country?
Designed to be reminiscent of the Sputnik satellite, launched into space in 1957, the Berlin TV Tower was constructed 12 years later with the help from Swedish engineers.
#3. Two soft drinks produced in East Germany as alternatives to Coca Cola are still available today – the most popular is Vita Cola. What is the other?
Introduced in 1967, following a specific request from the Socialist Unity Party of East Germany, Club Cola was the Coca Cola of East Germany and is available today. Reintroduced to the market in 1992, it is produced by the Spreequell Mineralbrunnen GmbH.
#4. Who was the first and last President of the German Democractic Republic?
The first and only president of East Germany was Wilhelm Pieck. Following his death in 1960 the office was abolished and replaced by the collective Council of State, whose chairman, and thus most prominent member, was SED First Secretary Walter Ulbricht.
#5. When the Berlin Wall was constructed in 1961, the barbed wire used to construct the first version of this barrier was supplied in part by companies from which one of these Western countries?
The barbed wire required for ‘Operation Rose’ (as the operation to construct the Berlin Wall was known by the East German government) would be bought in bulk from several different manufacturers in West Germany and in Great Britain. As to avoid suspicion whilst planning to envelop West Berlin it was seen as necessary to distribute the acquisition of the quantity needed to a number of innocuous looking East German purchasers, who negotiated the deals directly.
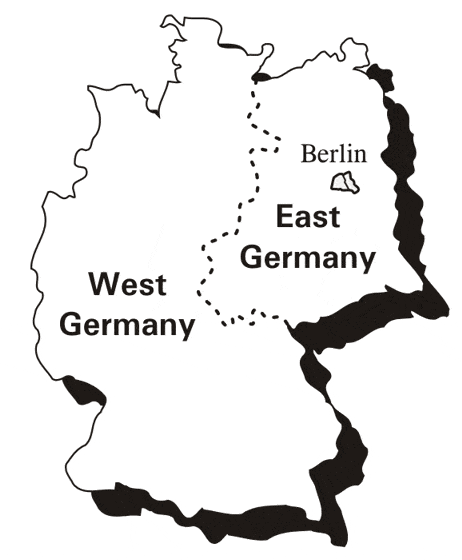
#6. Which of these German german states was NOT part of the German Democratic Republic?
Although Saxony is part of the former East, Lower Saxony is the name given to the region in the north west of Germany – the second-largest state by land area, with 47,624 km2 (18,388 sq mi), and fourth-largest in population (7.9 million) among the 16 Länder federated as the Federal Republic of Germany. Its capital is Hanover.
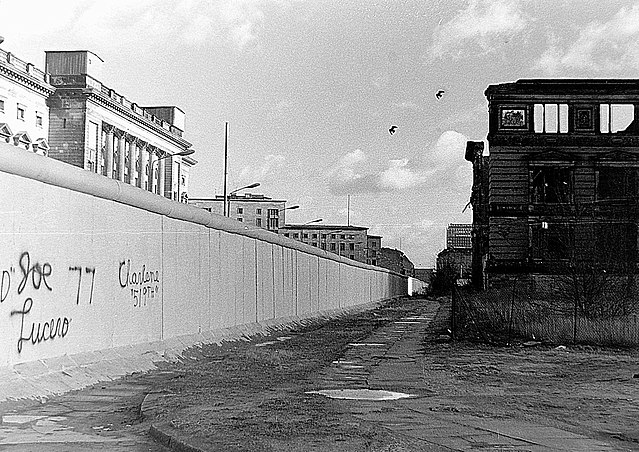

#7. The Berlin Wall memorial currently lists how many people who died whilst trying to escape the republic?
In total there are currently 140 known victims of the Berlin Wall listed by the Berlin Wall Memorial Foundation, of these 101 were people shot whilst trying to escape from the East. The remaining 39 victims were either border guards, people from East or West without escape plans – and one Soviet soldier.

#8. What was the English title of the party song of the East German Socialist Unity Party, Das Lied der Partei?
Although not the official national anthem of East Germany – that was Auferstanden aus Ruinen (German for “Risen from Ruins”) – Das Leid der Partei was used by the political party that ruled the country from 1949 until 1990 and never far away. It is best known by the first line of its chorus: Die Partei, die Partei, die hat immer recht (English: The Party, the Party, is always right), thus sometime reduced to the English title: The Party Is Always Right.

#9. According to East German propaganda, what were US planes dropping into the country in the 1950s to damage crops and trigger a famine?
After World War II, nearly half of all potato fields in the Soviet-occupied zone were infested by the potato beetle by 1950. In East Germany in the 1950s, the insect came to be known as Amikäfer, a neologism for Amerikanischer Käfer (the American beetle). Propaganda posters showed the beetle being dropped from American planes with the caption Kampf für den Frieden (The battle for peace). A letter was issued to “the people of the world”, stating that “the beetles are smaller than the atomic bomb… but they are also a weapon of the US imperialists in the fight against the peace-loving workers and peasants of East Germany.”
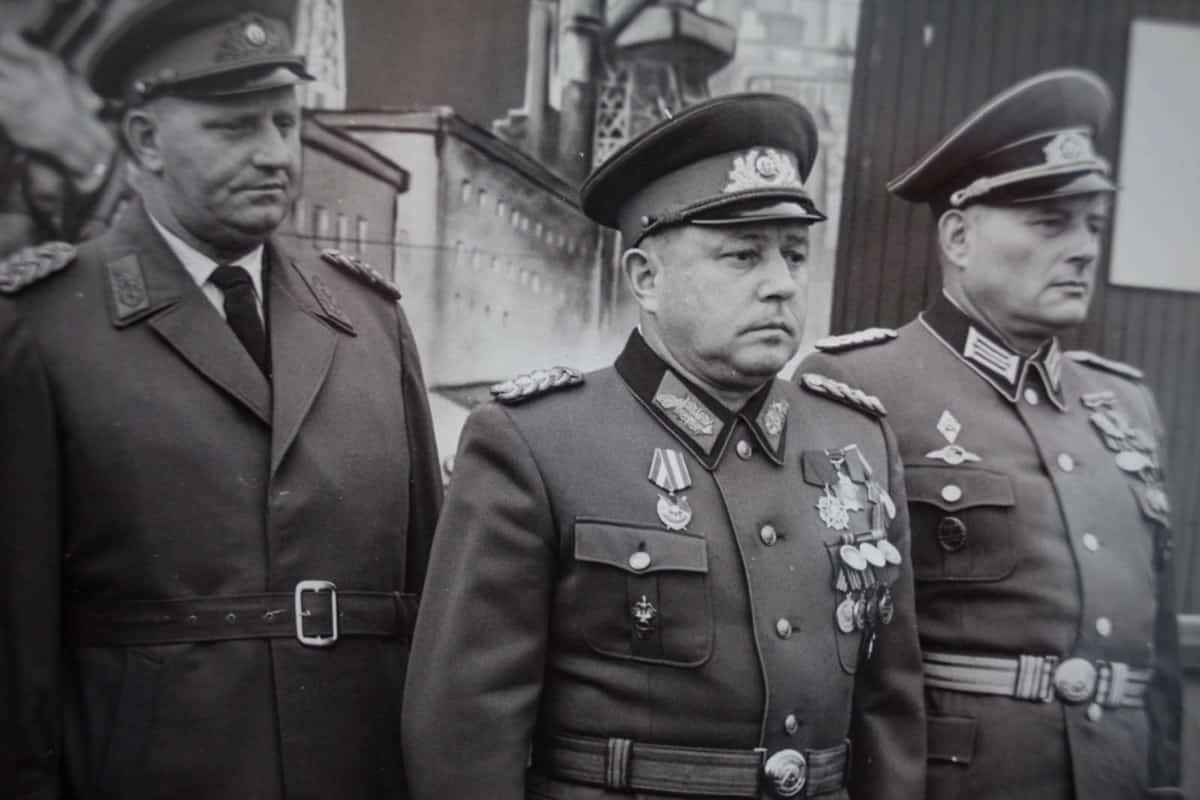

#10. True of False: the East German State Police – headed by Erich Mielke (pictured) – operated their own Department of Pornography.
TRUE: While pornography was banned in East Germany, the country’s state security police maintained a department of 160 people from 1982 that managed to make 12 pornographic movies before the ‘Fall of the Berlin Wall’ in 1989.

#11. Which non-East Bloc company had a contract to supply the East German government with vehicles for Politburo members?
Sweden remained neutral during the Cold War period and thus was able to supply material and services to both side of the international conflict. While the ordinary East German might get a Trabant (if lucky), the more important members of the ruling Politburo would be chauffeuered around in luxurious Swedish Volvos. The decision was largely a matter of capital. When faced with importing Tatra limos from the Socialist brotherland of Czechoslovakia, the government opted for the quiter, more reliable – and cheaper – Volvo from neutral Sweden.

#12. True or False: the East German Trabant was named after the Sputnik satellite?
TRUE: The German word Trabant, derived from the Middle High German drabant, means ‘satellite’ or ‘companion’.[a] The car’s name was inspired by the Soviet Sputnik satellite, which launched in the same year as the first Trabants rolled off the production line.
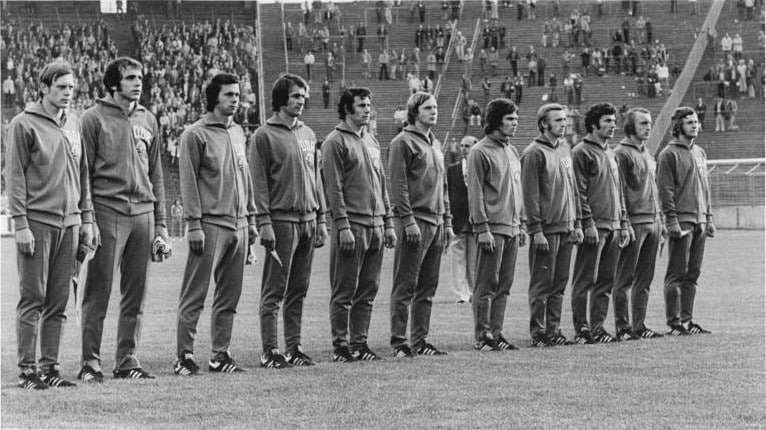

#13. True or False: When, on June 22nd 1974, East Germany played against West Germany in the football World Cup, East Germany won.
TRUE: The game in Hamburg, in front of 62,000, was won 1–0 by East Germany courtesy of a goal by Jürgen Sparwasser. East Germany was eventually eliminated in second group stage while West Germany won the World Cup.

#14. During a state visit to the DDR in 1972, Cuban leader Fidel Castro promised to donate an island to East Germany; the island would be renamed after which Communist leader?
Ernst Thälmann Island is a 15km long and 500mwide Cuban island in the Gulf of Cazones that is named after German Communist Party leader, Ernst Thälmann. Thälmann was in charge of the party in 1933 before being arrested by the Nazis and imprisoned in Buchenwald Concentration Camp, where he would die in 1944.

#15. In 1950, roughly 5% of the East German population was considered non-religious. What percentage had that risen to by 1989?
Although the East German government initially tried to fight against religious influence in the country, from 1953 the decision was made to try to co-opt the power of religious life and provide a Socialist alternative. By 1989, 70% of the population was classified as non-religious, as opposed to 15% in 1950 – making the country one of the biggest non-religious countries in the world.

#16. Who was the East German Ampelmann?
The Ampelmann was the symbol shown on pedestrian signals in East Germany, still visible across former East Germany today. After the ‘Fall of the Berlin Wall’, the symbol acquired cult status and became a popular souvenir item in the tourism business.

#17. What was the name of the East German youth organisation for children aged 6 to 14?
From age 6 to 14, East German children could join the Young Pioneers organisation – followed by the Free Germany Youth from 14 to 25. Around 75% of children would join the Free German Youth, with membership based on previous involvement with either the Young Pioneers or Ernst Thälmann Pioneers (the sister organisation of the YP).

#18. The ‘Fall of the Berlin Wall’ in November 1989 was triggered by an East German government announcement to grant what:
When on November 9th 1989, East German press officer Gunter Schabowski addressed members of the international press in East Berlin, in the event that led to the ‘Fall of the Berlin Wall’, it was to announce the issue of travel visas by the East German government. A process that was expected to take some time, although due to Schabowski’s fumbled response to a reporters question – and the unstoppable pace of news media at the time – this message was conveyed to the public as the opportunity to immediately leave the country.
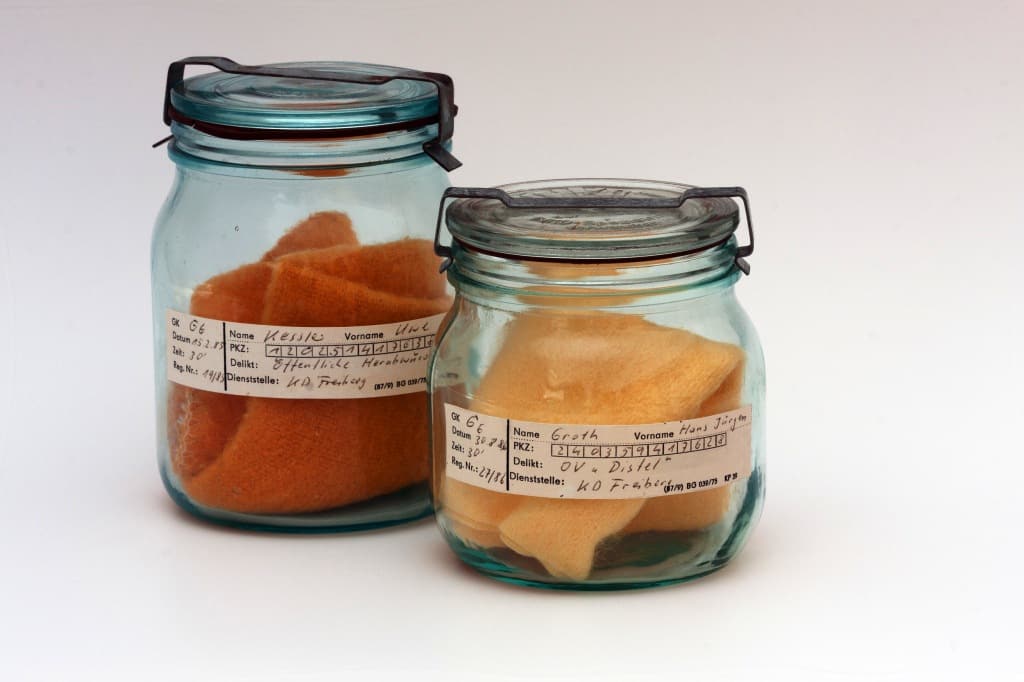

#19. The East German STASI used these jars to collect what:
As a way of tracking and identifying dissidents in the country, the East German state police collected smells is these jars from the people they would interrogate. Often this involved laying a cloth over the chair that the suspect was forced to sit on, with the palms of their hands facing down, so to sweat into the cloth. This would then be sealed in a jar and store to be used at a later date for identification purposes.

#20. True or False: in East Germany there were milk stations for women to donate breast milk for mothers who could not produce it themselves or were sick?
TRUE: In East Germany, there was a mother’s milk station in every municipality, which would pick up pumped milk (often by bicycle) and pay families for it. 1989 was a record year when GDR mothers donated 200,000 liters of milk.
Results
Not bad. Not bad at all!
It seems you can easily claim to be an expert on the history of East Germany.
Perhaps a career as a tour guide or local historian awaits?
If you’re looking to learn more, consider one of our Republic of Fear tours covering the major and minor sites in Berlin related to the history of East Berlin and life behind the Iron Curtain.
Oh no, you managed less than 90%.
Don’t worry, the questions were meant to be hard.
Next time you’re heading to Berlin make sure to check out our history tours, where you’re guaranteed to learn more about East Germany. Specifically our Republic of Fear tour might be just what you are looking for.
Our Related Private Tours
Learn more about the Battle of Berlin and explore this urban battlefield with our Battle of Berlin tours.
Learn more about the history of Nazi Germany and life in Hitler’s Third Reich with our Capital Of Tyranny tours.
Learn more about the history of East German and life behind the Iron Curtain with our Republic Of Fear tours.
Learn more about the history of Prussia and the life of Frederick the Great with our Glory Of Prussia tours.
Learn more about SS ‘Protective Custoday’ on our Sachsenhausen Concentration Camp Memorial tours.
















